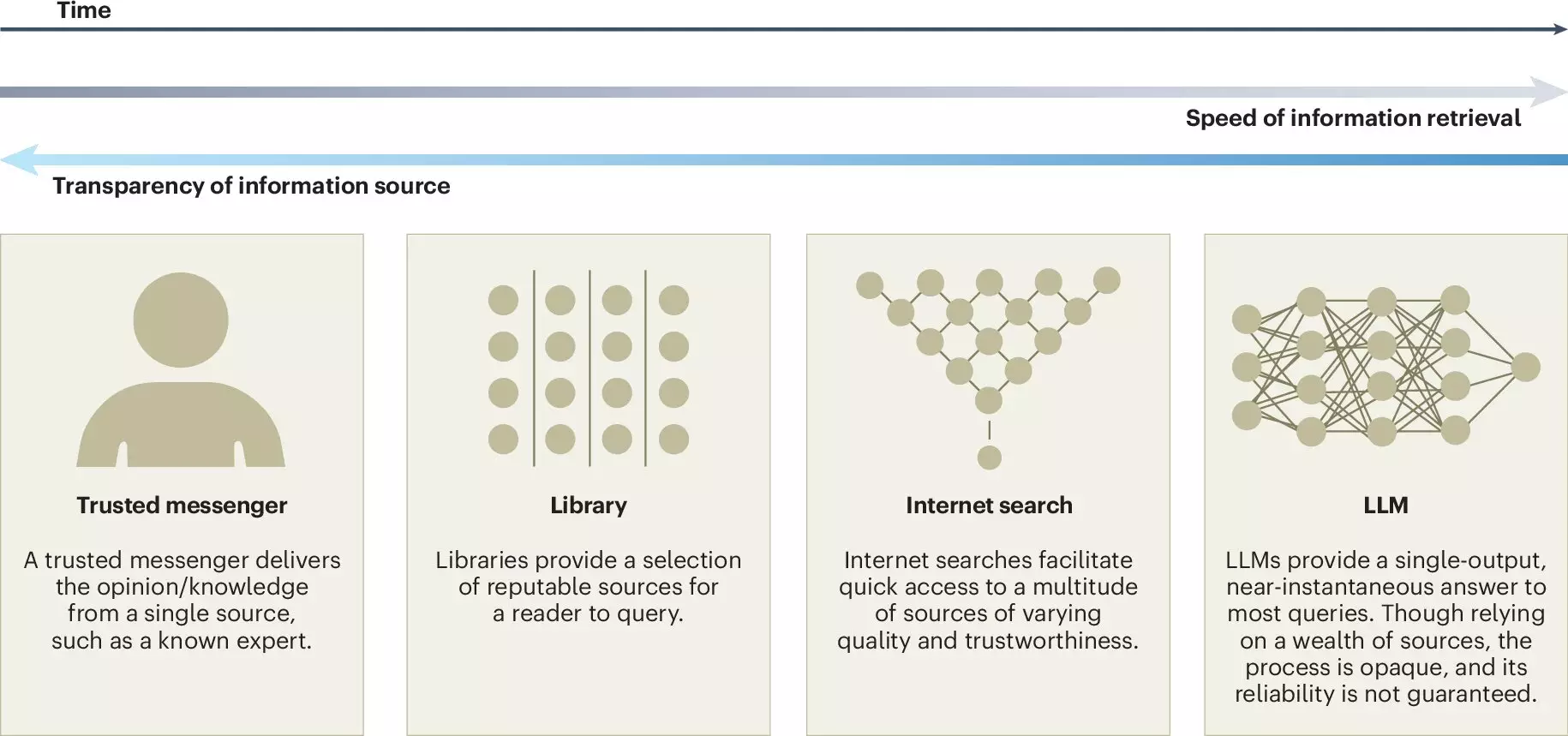
In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the way we interact with technology and information. With tools like ChatGPT becoming prevalent, these models have integrated seamlessly into our daily routines, enhancing various aspects of communication and decision-making. An insightful article has emerged from a collaborative effort between researchers at Copenhagen Business School and the Max Planck Institute for Human Development, shedding light on both the beneficial opportunities and the potential risks posed by the proliferation of LLMs. The article serves as a guide for researchers and policymakers aiming to maintain the delicate balance between leveraging LLMs and preserving human collective intelligence.
Collective intelligence refers to the combined knowledge and skills of a group, which can often exceed the capabilities of any individual member. This phenomenon manifests in various forms, from small collaborative teams within organizations to broad online communities such as Wikipedia and Reddit. When faced with challenges or decisions, people often turn to collective intelligence by consulting colleagues, friends, or digital communities, intuitively understanding that a collaborative approach can yield more comprehensive solutions.
The role of LLMs in enhancing collective intelligence is particularly noteworthy. These AI systems utilize vast datasets, generating insights and information that can sharpen decision-making processes. By offering diverse viewpoints and summarizing complex data, LLMs have the potential to enrich discussions, drive innovation, and foster more inclusivity in group settings.
One of the notable advantages of implementing LLMs in collective processes is their ability to democratize access to information. Language barriers can often hinder participation in discussions—LLMs can mitigate this issue through automatic translation services and writing assistance, allowing voices from diverse backgrounds to emerge. Additionally, LLMs can streamline the ideation phase in collaborative settings, facilitating faster consensus through thoughtful filtering of information and synthesis of different perspectives.
By enhancing accessibility and amplifying diverse voices, LLMs can foster a culture of collective problem-solving. Whether in an academic setting or a corporate environment, the integration of LLM technologies can lead to richer, more informed discussions, driving teams toward innovative solutions.
However, the integration of LLMs is not without its drawbacks. One significant concern is the erosion of intrinsic motivation among contributors in collective knowledge platforms like Wikipedia. If users come to overly depend on proprietary LLM outputs, there may be a diminished incentive for individuals to contribute their own knowledge and insights, effectively threatening the open-source ethos that underpins such community platforms.
Moreover, the phenomenon of false consensus looms large. LLMs, often trained on content from the internet, may amplify dominant voices while sidelining minority perspectives. This could lead to a mistaken belief that a majority opinion exists when, in reality, diverse viewpoints are marginalized. Experts warn that this could foster a limited understanding of complex issues and reinforce societal biases.
The article underscores the urgent need for transparency in the development of LLMs. Researchers advocate for greater clarity regarding the sources of data used to train these models and suggest that auditing practices be employed to assess their outputs critically. Ensuring that developers are held accountable for the influences shaping LLM behavior is paramount in promoting ethical AI practices.
Additionally, the article provides thought-provoking insights into the relationship between human input and LLM functionality. The development of LLMs must prioritize diverse representation, ensuring that the data drawn from various contexts accurately reflects a wide array of human experiences. By focusing on inclusive development, LLMs can become tools that genuinely support collective intelligence rather than stifle it.
The article provokes further inquiry into several pressing questions regarding LLMs. For instance, how can we prevent the homogenization of knowledge spurred by dependence on LLM outputs? How can credit for collective outcomes be fairly distributed, particularly when the lines between human and AI contributions blur? Addressing these research avenues will be pivotal in shaping responsible LLM deployment.
While LLMs offer remarkable opportunities for enhancing collective intelligence by democratizing information and facilitating collaboration, they also pose significant risks that must be acknowledged. The insights from the interdisciplinary team illuminate the path forward, urging researchers, developers, and policymakers to consider how best to integrate these advanced technologies into our collective processes while safeguarding against potential harms. Ultimately, the responsible development of LLMs can pave the way for a future where technology and humanity work hand in hand to solve complex challenges.