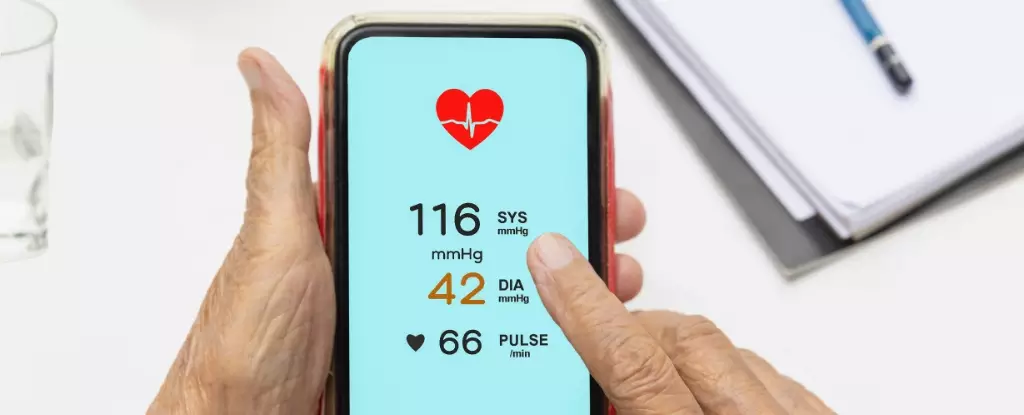
High blood pressure, medically known as hypertension, is more than just a number; it’s a pervasive health issue that affects millions globally, often without their knowledge. This silent killer can lead to serious medical emergencies, such as heart attacks and kidney failures, making early detection crucial. Traditional methods of monitoring blood pressure involve cumbersome trips to healthcare facilities or the use of specialized medical devices, which can be inaccessible for many, particularly in underserved areas. However, recent technological advancements hint at a transformation in how we can monitor blood pressure efficiently and accurately, using a device that many already carry: the smartphone.
A groundbreaking application developed by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh has emerged as a potential game-changer in blood pressure monitoring. Unlike conventional devices, this innovative Android app leverages the integrated sensors—like accelerometers, cameras, and touch sensors—of modern smartphones. This technology allows users to measure their arterial pressure remotely and intuitively without needing excessive medical equipment. “Most people have smartphones, but many lack access to regular healthcare services,” explains Ramakrishna Mukkamala, a biomedical engineer involved in the project. This realization underscores the app’s significance for individuals in low-resource settings.
The app operates on the fundamental principles of how traditional blood pressure cuffs work. Typically, a sphygmomanometer—an inflating cuff—constricts an artery to determine systolic and diastolic pressures. In contrast, this smartphone app calculates pulse pressure using gravity and touch pressure exerted by the user’s thumb on the touchscreen. The method presents a remarkable shift, as it combines medical science with the conveniences of everyday technology.
Utilizing simple hand movements and a series of finger taps, users interact with their smartphones to produce the necessary measurements. The app instructs users on how to position their hands to change blood flow, which, in effect, allows the phone to gather the needed data points for an accurate readout. Biomedical engineer Vishaal Dhamotharan explains that when a user elevates their hands, a hydrostatic pressure change occurs in the thumb. The app utilizes the smartphone’s accelerometer to factor in this change, providing a relative pulse pressure reading without the need for a traditional cuff.
In preliminary tests involving 24 participants, the app managed to achieve a level of accuracy that is within a margin of approximately 8 mm Hg. Although further refinement is needed, the researchers see the potential for improved accuracy as development continues. Adjusting societal perspectives around pulse pressure as a legitimate blood pressure metric is also on the agenda for the team.
The implications of this innovation extend beyond mere convenience. If successful, it could democratize access to vital health information, particularly in marginalized communities lacking adequate healthcare infrastructure. This technology embodies the essence of preventative health: empowering individuals to monitor their health independently and detect issues before they escalate into emergencies.
According to Sanjeev Shroff, another lead researcher from the University of Pittsburgh, the long-term goal is to create a cuffless device that requires no external calibration—a feat that, until now, has remained elusive in the field of medical technology. Current aim is to first establish this smartphone-based app as a reliable tool for monitoring blood pressure, gradually working towards its acceptance in everyday health management.
This innovative app signifies a potential paradigm shift in how we understand and monitor hypertension. By harnessing readily available technology, the app not only simplifies the process of blood pressure monitoring but also addresses critical gaps in healthcare access. The implications are enormous: improved monitoring could lead to better health outcomes, a reduction in life-threatening conditions related to hypertension, and ultimately, a healthier society. As research and development progresses, this smartphone app may well play a pivotal role in the ongoing battle against one of the world’s most significant health challenges.