In the accelerating field of renewable energy, particularly in solar cells and light-emitting diodes (LEDs), a crucial hurdle is the management of energy loss mechanisms. Among these, exciton-exciton annihilation stands out as a significant factor that diminishes the performance of these devices, thus stalling the broader adoption of clean energy technologies. As sources of light and energy, solar cells and LEDs show vast potential; yet, they are often undermined by the rapid decay of energy efficiency—often a result of excited-state dynamics. How can researchers effectively balance energy loss and desired output? The quest to mitigate these losses brings us to a fascinating intersection of quantum mechanics and photonic engineering.
The Role of Cavity Polaritons in Combating Energy Loss
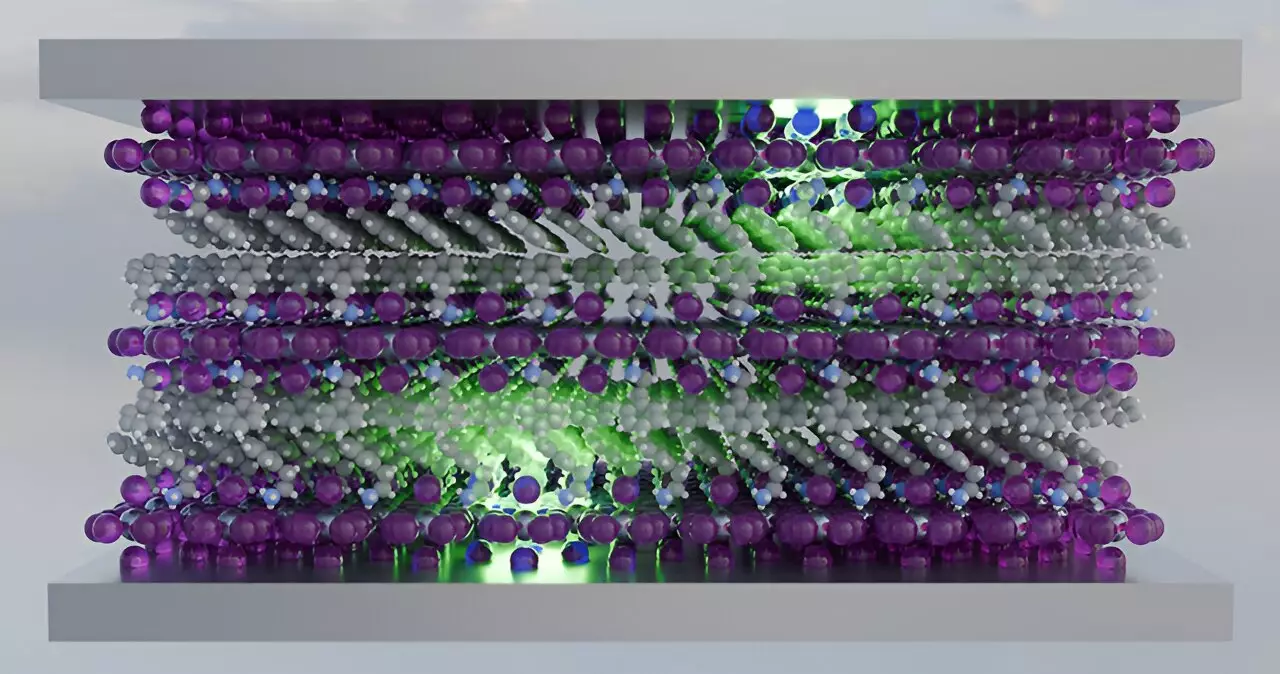
Recent research from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and the University of Colorado Boulder provides compelling insights into a novel approach to address the critical issue of exciton-exciton annihilation. The scientists employed cavity polaritons, which are intriguing hybrid states formed when photons are trapped between two mirrors. This innovative strategy effectively lowers the chances of energy dissipation during exciton interactions. By manipulating the physical distance between these mirrors, researchers were able to exhibit finer control over the exciting dynamics within the excited states of materials like the 2D perovskite (PEA)2PbI4 (PEPI).
At the heart of this experiment was transient absorption spectroscopy, a technique that allowed researchers to measure how effectively excitation energy could be managed in these new hybrid states. This careful manipulation of the cavity design not only showcased the power of physical arrangements but also highlighted the potential to enhance the efficiency of devices that use these perovskite materials. By lessening the impact of energy losses, the research hints at a future where solar devices and LEDs could operate at unprecedented levels of efficiency.
Transforming excited-state dynamics through strong coupling
What makes the coupling of excitons with cavity modes particularly powerful is the phenomenon of strong coupling. In essence, this interaction allows for the rapid interchange between excitonic and photonic characteristics, permitting polaritons to traverse each other without succumbing to annihilation—an occurrence that would devastate traditional exciton interactions. Thus, the research team has opened up avenues for managing how long these excitons spend in their ‘excited’ forms.
The implications are profound. By tuning the strength of this coupling, researchers can dictate how these hybrid particles behave, creating a dynamic framework for experimenting with excited-state kinetics. This finding marks a significant leap forward in our understanding of the quantum interactions that govern energy efficiency, opening doors to real-world applications where performance can be measurably improved.
Insight and Implication for Future Research
Jao van de Lagemaat, the director of chemistry at NREL, encapsulated the excitement of these findings: If we can truly gain control over exciton dynamics in practical applications, the door opens to energy-efficient technologies that fundamentally overhaul how we generate and consume energy. The ability to limit exciton losses could pave the way for a new era of optoelectronic devices that use less energy and yield greater performance. This offers tantalizing prospects in a world where energy demands continue to rise.
Moreover, the work done by Rao Fei and his colleagues serves as an illustrative example of how innovative approaches to established problems can lead to serendipitous discoveries. The transformative dynamics revealed through simple experimental designs have strikingly significant implications that extend beyond the confines of individual materials to the broader landscape of renewable energy technologies.
In addressing energy loss dynamics, this research isn’t merely an academic exercise but rather a cornerstone for future innovations that could revolutionize how we harness and utilize energy. The road ahead requires sustained investment in both theoretical exploration and practical applications, yet the potential rewards—a substantial reduction in energy consumption and enhanced device efficacy—make the pursuit worthwhile.