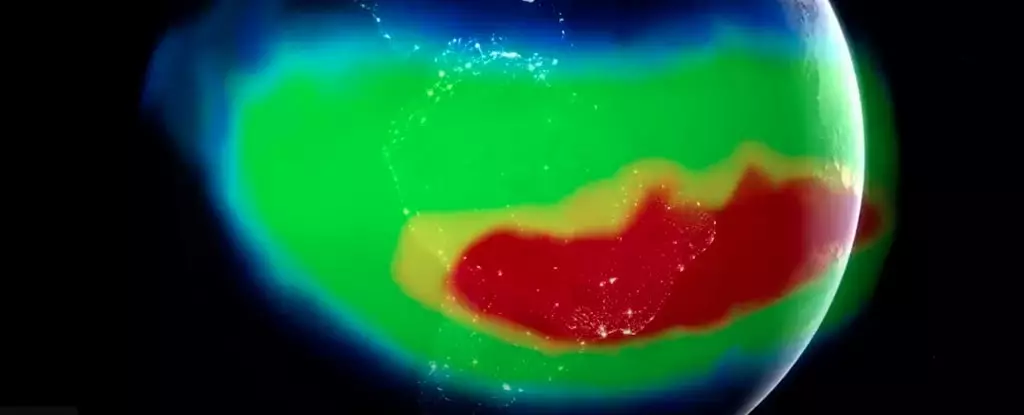
In an eye-catching twist of nature, scientists are closely monitoring a perplexing phenomenon known as the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA). Stretching between South America and southwest Africa, this unusual area is characterized by a significant reduction in magnetic intensity, leading to serious implications for both our planet and the technology orbiting it. While Earth may seem stable below our feet, the magnetic landscape above is far from straightforward—a reality that raises concerns and curiosity among researchers worldwide.
The SAA has the uncanny ability to intrigue and alarm, primarily because it poses unique challenges for the satellites and spacecraft that pass through its weakened magnetic shield. Unlike life on the surface, these machines are particularly vulnerable to the ramifications of a compromised magnetic field, which allows exposure to a barrage of solar particles. This magnetic ‘dent,’ dubbed a ‘pothole in space’ by NASA, intrudes on our technological operations, ultimately prompting a reevaluation of how we navigate our journeys beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
Effects on Spacecraft and Technology
Operating spacecraft in low Earth orbit necessitates enhanced caution, especially as these vehicles routinely traverse the SAA. The depleted magnetic field in this region can lead to a myriad of issues, from minor data glitches to potentially catastrophic failures in critical systems. It’s a reminder of the fine line NASA and other space agencies walk as they attempt to push the boundaries of exploration while safeguarding their investments in technology.
Satellite operators, faced with these challenges, often devise preemptive measures that involve shutting down or recalibrating instruments before entering the anomaly zone. This precaution underscores the severity of the risks—an unanticipated hit from high-energy protons can wreak havoc on sensitive electronics, underscoring the delicate nature of our modern technological landscape.
However, the SAA also offers an unprecedented opportunity for scientific exploration. Rather than view this anomaly solely as a complication, researchers acknowledge that it is a unique window into understanding Earth’s magnetic field dynamics. As NASA’s resources and expertise converge to study the SAA, we stand to gain deeper insights into the natural forces sculpting our planet’s magnetic environment.
Geophysical Foundations of the Anomaly
Delving into the origins of the SAA reveals a complex interplay of geophysical forces. The magnetic field of Earth is primarily generated by the movement of molten iron within the outer core, a molten expanse influenced by the solid Earth above. This process, however, is not uniform. Recent studies have posited that beneath the African continent lies a geological anomaly known as the African Large Low Shear Velocity Province—a geological formation that may be contributing to the SAA.
Researchers suggest that this irregularity is disrupting the conventional magnetic field generation, leading to the pronounced weakening observed. The combined effects of this geological formation and the tilt of the planet’s magnetic axis create an environment wherein localized fields with opposite polarity emerge, further reducing magnetic intensity in the SAA. The situation is akin to wrestling with a chaotic puzzle, revealing just how interrelated our planet’s interior processes are with its magnetic behavior.
The Evolving Nature of the SAA
One of the most fascinating aspects of the SAA is its dynamic character. Recent findings have indicated that not only is the anomaly drifting; it appears to be in the process of bifurcating. Emerging data suggest that the SAA might split into two separate cells that each manifest their own unique magnetic properties. This transformation could signal a significant shift in how we understand the anomaly’s effects on both terrestrial life and satellite operations.
To further complicate the narrative, researchers speculate that the SAA may have roots extending back millions of years, positing it as a recurring geological phenomenon rather than a recent anomaly. The ramifications of this revelation could turn our understanding of Earth’s magnetic history on its head, suggesting that our planet’s magnetic field undergoes shifts that are more frequent than previously thought.
The Future of the South Atlantic Anomaly
As studies continue to unfold, the SAA represents a prime example of the delicate balance between risk and opportunity that characterizes contemporary scientific inquiry. With its potential for causing disruptions in technology layered with its complexity, the phenomena warrants meticulous observation. NASA’s commitment to monitoring the SAA exemplifies a proactive approach to understanding not only the anomaly itself but also its broader implications on Earth’s magnetic field health.
By delving into this magnetic enigma, scientists not only inform our current understanding but also lay the groundwork for future exploration. What remains to be seen is how the story of the SAA continues to evolve and what it will unveil about our planet’s intricate systems. As methods and technologies advance, the narrative of the South Atlantic Anomaly will undoubtedly illuminate new horizons of understanding in our quest to decipher the cosmos.